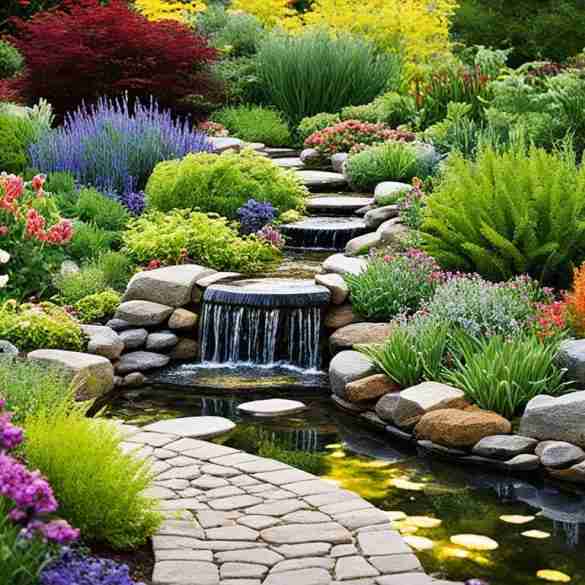
Welcome to Sustainable Home Magazine, where we provide you with valuable insights and tips for creating a greener and more sustainable living environment. In this article, we will explore the design and implementation of a rain garden, a sustainable landscaping solution that promotes water conservation techniques and helps manage rainwater runoff effectively.
Rain gardens are innovative features designed to capture, store, and filter rainwater, reducing stormwater runoff and promoting groundwater recharge. By implementing a well-designed rain garden, you can contribute to sustainable water management practices and create a more resilient landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- Rain gardens are sustainable landscape features that manage rainwater effectively.
- They capture, store, and filter rainwater, reducing stormwater runoff.
- Proper design principles and native plant selection are vital for the success of a rain garden.
- Rain gardens offer benefits such as water pollution reduction and support for biodiversity.
- Regular maintenance is essential for the long-term health of a rain garden.
The Design Principles of Rain Gardens
Choosing the right location is critical for the success of a rain garden. It should be placed where water naturally collects, avoiding utility lines or shallow foundations. The size and shape of the rain garden should be determined by the size of the contributing area and the volume of water runoff. Proper soil preparation, including organic matter incorporation, is crucial. Mulching the surface and regular maintenance are also important.
When designing a rain garden, consider these key principles:
- Location: Choose a spot where water naturally accumulates, such as near downspouts or at the base of a slope. Avoid areas with utility lines or shallow foundations.
- Size and Shape: Assess the contributing area and volume of water runoff to determine the appropriate size and shape of the rain garden. A larger rain garden will be able to handle more runoff.
- Soil Preparation: Adequate soil preparation is vital for a healthy rain garden. Use a mix of organic matter, such as compost, to improve soil structure and drainage.
- Native Plant Selection: Select water-absorbing plants native to your region. They are well-adapted to local conditions and provide habitat for wildlife.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch on the surface of the rain garden to help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and insulate the soil.
- Regular Maintenance: Maintain the rain garden by removing weeds, pruning plants as needed, and monitoring for any signs of erosion or drainage issues.
Proper rain garden design ensures effective water management, promotes biodiversity, and contributes to a more environmentally-friendly garden. By following these design principles, you can create a beautiful and functional rain garden that helps conserve water and supports local ecosystems.

Selecting Native Plants for Rain Gardens
When it comes to designing a rain garden, selecting the right plants is key to its success. Native plants are particularly well-suited for rain gardens because they are adapted to the local climate, soil conditions, and water availability. Not only do these plants enhance the aesthetic appeal of the garden, but they also provide numerous ecological benefits.
Native plants for rain gardens:
- Increase water absorption
- Prevent soil erosion
- Support local biodiversity
- Provide habitat and food sources for wildlife

Selecting a mix of native plant species with varying heights, bloom times, and textures is essential to create visual interest and maximize ecological benefits. Here are some examples of native plants that are commonly used in rain gardens:
| Plant Name | Height | Bloom Time | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rudbeckia hirta (Black-eyed Susan) | 2-3 feet | Summer | Medium |
| Echinacea purpurea (Purple Coneflower) | 2-4 feet | Summer | Coarse |
| Asclepias tuberosa (Butterfly Milkweed) | 1-2 feet | Summer | Fine |
| Lobelia siphilitica (Great Blue Lobelia) | 2-3 feet | Summer | Medium |
The combination of these native plants creates an inviting habitat for pollinators and other wildlife while also providing a visually appealing display in your rain garden.
Benefits of Using Native Plants
The use of native plants in rain gardens has a multitude of benefits. Not only do they help conserve water and prevent soil erosion, but they also support the local ecosystem by providing food and shelter for native birds, pollinators, and other wildlife. Additionally, native plants have deep root systems that improve water absorption, reducing the risk of flooding and promoting groundwater recharge.
By selecting native plants for your rain garden, you are not only creating a beautiful and resilient landscape but also contributing to the conservation of local biodiversity.

Creating a Plant List for Rain Gardens
When designing a rain garden, selecting the right plants is crucial for its success. You want to choose a diverse mix of trees, shrubs, grasses, and perennials that are well-suited to the specific site conditions and fulfill the ecological functions of a rain garden. Keep in mind that these plants should be able to tolerate both wet and dry conditions, as well as provide support for local wildlife.
Here are some examples of rain garden plants that are commonly used:
- River Birch (Betula nigra): With its attractive peeling bark, the river birch adds visual interest and thrives in wet soils.
- Redbud (Cercis canadensis): This native tree offers beautiful spring blooms and can tolerate a variety of soil conditions.
- Buttonbush (Cephalanthus occidentalis): Known for its unique globular flowers, this shrub is a favorite of butterflies and pollinators.
- Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum): A tall grass that adds a vertical element to the garden and provides habitat for birds.
- Bee Balm (Monarda spp.): This perennial plant produces vibrant flowers that attract hummingbirds and bees.
These are just a few examples, and there are many more rain garden plants to choose from. The key is to select plants based on their ability to thrive in your specific climate, soil conditions, and sunlight exposure. By incorporating a variety of plants with different heights, textures, and bloom times, you can create a visually appealing and ecologically beneficial rain garden.
Remember, the plants you choose for your rain garden will play a vital role in stormwater management and supporting local biodiversity. It’s important to take the time to research and select the right plants for your specific rain garden project.

By incorporating native plant species that are well-adapted to your local ecosystem, you can create a rain garden that not only helps manage stormwater runoff but also provides valuable habitat for birds, butterflies, and other wildlife.
Example Rain Garden Plant List
| Plant Type | Common Name | Scientific Name | Height | Sunlight Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | River Birch | Betula nigra | 40-70 feet | Full sun to part shade |
| Tree | Redbud | Cercis canadensis | 20-30 feet | Full sun to part shade |
| Shrub | Buttonbush | Cephalanthus occidentalis | 6-12 feet | Full sun to part shade |
| Grass | Switchgrass | Panicum virgatum | 3-6 feet | Full sun |
| Perennial | Bee Balm | Monarda spp. | 2-4 feet | Full sun to part shade |
Benefits of Rain Gardens
Rain gardens offer numerous benefits that make them a valuable addition to any landscape. These gardens play a crucial role in stormwater management, water conservation, and urban water management. By harnessing the power of nature, rain gardens provide a sustainable solution that benefits both the environment and property owners.
Reducing Water Pollution
Rain gardens act as natural filtration systems, reducing water pollution by trapping sediments, chemicals, and pollutants from rainwater runoff. The plants and soil in the rain garden work together to remove harmful substances, preventing them from entering waterways and polluting our rivers, lakes, and oceans.
Preventing Erosion
Rain gardens help prevent erosion by absorbing and slowing down the flow of water. The deep-rooted native plants in the garden stabilize the soil, reducing the risk of erosion caused by heavy rainfall. This not only protects the integrity of the garden but also prevents soil erosion in surrounding areas.
Supporting Local Biodiversity
Rain gardens create diverse habitats for native plants, insects, birds, and other wildlife. The combination of native plants with varying heights, bloom times, and textures provides food and shelter for local species. By supporting local biodiversity, rain gardens contribute to the overall health and balance of ecosystems.
Nourishing Plants with Rainwater in a rain garden design
Rain gardens collect and store rainwater, which is then slowly released into the soil. This allows the plants in the garden to access the water they need for growth and survival, even during dry periods. By conserving and utilizing rainwater, rain gardens contribute to water conservation efforts.
Reducing Flooding Problems
Stormwater runoff from paved surfaces can overwhelm drainage systems and lead to flooding. Rain gardens help alleviate this issue by capturing and storing rainwater, reducing the volume and velocity of runoff. This helps mitigate flooding problems and reduces the strain on municipal stormwater infrastructure.
Preventing Mosquito Breeding in your rain garden design
Rain gardens are designed to drain excess water within a few days, preventing the accumulation of stagnant water. Stagnant water is a breeding ground for mosquitoes, which can transmit diseases. By reducing standing water, rain gardens help control mosquito populations and promote a healthier environment.
Overall, rain gardens offer a multitude of benefits, including water pollution reduction, erosion prevention, support for local biodiversity, more efficient water use, flood mitigation, and mosquito control. These gardens provide a sustainable solution to stormwater management and contribute to healthier urban water systems.

Common Issues and Considerations in Rain Garden Design
Designing a rain garden involves several considerations to ensure its effectiveness and longevity. By addressing common issues such as poor drainage, erosion, steep slopes, and high costs, you can create a functional and sustainable rain garden. Here are some essential considerations to keep in mind during the design process:
Poor Drainage
Ensuring proper drainage is crucial for the success of a rain garden design. Conducting a water percolation test will help determine the soil’s drainage rate and inform the design and construction of the rain garden. If the soil has poor drainage, additional measures such as installing drainage pipes or incorporating soil amendments may be necessary.
Erosion
Erosion can occur when water runoff is not effectively managed within the rain garden. To prevent erosion, consider incorporating erosion control measures such as strategically placed rocks or gravel to stabilize the soil. Planting deep-rooted native vegetation can also help stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
Steep Slopes for Rain Garden Design
Designing a rain garden on steep slopes may present challenges in managing water flow and preventing soil erosion. Terracing the rain garden or incorporating retaining walls can help address this issue. Consulting with a landscape architect or engineer can ensure the safe and effective incorporation of a rain garden on steep terrain.
High Costs
Rain garden construction costs can vary depending on factors such as size, materials, and labor. Consider designing a rain garden that fits within your budget without compromising its functionality. Opting for locally sourced materials and utilizing volunteer or community-driven initiatives can help reduce costs while still achieving the desired environmental benefits.
By addressing these common issues and considering site-specific factors, you can design a rain garden that effectively manages stormwater runoff, supports the environment, and enhances your landscape.
| Common Issues | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Poor Drainage | Conduct a water percolation test Consider drainage pipe installation |
| Erosion | Incorporate erosion control measures Plant deep-rooted native vegetation |
| Steep Slopes | Terrace the rain garden Incorporate retaining walls |
| High Costs | Design within your budget Utilize locally sourced materials |
Determining rain garden design Size and Depth
When designing a rain garden, it’s crucial to consider the appropriate size and depth to ensure its effectiveness in managing rainwater runoff. The size and depth of a rain garden depend on several factors that influence its functionality and efficiency.
The first consideration when determining rain garden size is the drainage area it will serve. This includes the surface area that contributes runoff to the rain garden. To achieve optimal results, a general guideline is to have a rain garden area equivalent to approximately five times the drainage area.
The infiltration rate of the soil also plays a significant role in rain garden sizing. The capacity of the soil to absorb and store water affects the volume of runoff that can be effectively managed by the rain garden. Soils with higher infiltration rates can accommodate smaller rain gardens, while soils with lower infiltration rates may require larger rain garden sizes.
Another factor to consider is the size of the uphill drainage area. If the drainage area is large, it may generate substantial runoff volume, necessitating a larger rain garden to accommodate the flow of water effectively.
The amount of impervious surfaces, such as roofs, driveways, and sidewalks, within the drainage area also influences rain garden sizing. More impervious surfaces generate greater runoff, requiring a larger rain garden to prevent water overflow and ensure proper stormwater management.
It’s important to keep in mind that the volume and intensity of rainfall can vary. Depending on the climate and region, rain events can range from light showers to heavy storms. To account for these variations, it may be necessary to adjust the size or depth of the rain garden accordingly.
If space is limited and a larger rain garden is not feasible, other rainwater management techniques can be employed in conjunction with the rain garden to enhance its effectiveness. These may include installing rain barrels, redirecting downspouts to alternative locations, or using permeable paving materials to reduce the amount of runoff reaching the rain garden.
Overall, determining the size and depth of a rain garden requires careful consideration of the drainage area, soil infiltration rate, uphill drainage area, impervious surfaces, and local rainfall patterns. By ensuring an appropriately sized rain garden, you can maximize its effectiveness in capturing and managing rainwater runoff, promoting sustainable water management practices, and contributing to a healthier environment.

Proper Site Selection for rain garden designs
When it comes to rain garden success, choosing the right location is key. The site selection will determine the effectiveness of your rain garden in managing stormwater runoff and promoting water conservation. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Placement between impervious surfaces: Position your rain garden between two impervious surfaces, such as a roof and a lawn. This will ensure efficient capture and absorption of rainwater runoff, preventing it from flowing into storm drains.
- Away from utility lines and shallow foundations: Avoid locating your rain garden near underground utility lines or shallow foundations to prevent any damage during the construction or excavation process.
- Consider the flow of rainwater: Analyze the natural flow of rainwater on your property. Choose a location where water naturally collects, ensuring that it will efficiently drain into the rain garden and away from foundations or low-lying areas.
- Obstacles to avoid: Take note of potential obstacles such as underground utilities or tree roots that may hinder proper rain garden installation and functioning. It’s important to address these issues to ensure the long-term success of your rain garden.
Tip: Before digging, it’s essential to contact utility companies to locate any underground lines or cables. This will help you avoid any accidents or damage during the installation process.
By carefully selecting the site for your rain garden, you can optimize its effectiveness in managing stormwater runoff and promoting a sustainable landscape. The proper placement of your rain garden between impervious surfaces, consideration of rainwater flow, and avoidance of potential obstacles will ensure the success of your rainwater management efforts.
Creating a Rain Garden in Your Landscape
When it comes to rain gardens, the installation process plays a crucial role in their success. By following a few key steps, you can create a beautiful and eco-friendly rain garden that effectively manages rainwater runoff.
1. Selecting the Right Location for your rain garden design
The first step in creating a rain garden is to choose the ideal location in your landscape. Look for areas where water naturally collects, such as low-lying spots or areas near downspouts. Avoid utility lines or shallow foundations to prevent any potential issues during construction.
2. Determining the Size and Shape of the rain garden design
Once you’ve found the right location, it’s important to determine the size and shape of your rain garden. Consider the size of the contributing area and the volume of water runoff to ensure your rain garden effectively captures and manages rainfall. A natural and rounded shape is recommended for optimal water flow and aesthetics.
3. Preparing the Soil for a rain garden design
Proper soil preparation is crucial for a successful rain garden. Remove any existing turf or vegetation from the area and dig a shallow basin or depression to collect rainwater. Amend the soil with organic matter to improve drainage and create an ideal environment for the plants.
4. Installing the rain garden design
Now comes the exciting part – installing your rain garden! Start by lining the depression with an erosion-control fabric to prevent soil erosion. Next, add a layer of gravel or crushed stone for additional drainage. Finally, fill the basin with a mixture of compost and topsoil.
Once the installation is complete, it’s time to select and plant the appropriate vegetation. Choose native perennial plants that can tolerate both wet and dry conditions. Their deep roots will help absorb water and prevent erosion. Consider incorporating a variety of plants to create visual interest and support local biodiversity.
5. Additional Considerations for a rain garden design
As you finalize your rain garden, there are a few additional considerations to keep in mind. Pay attention to the edges of your rain garden, ensuring a smooth transition with the surrounding landscape. If your landscape has slopes, hillside stabilization techniques may be necessary for effective rain garden functionality. Additionally, consider incorporating focal points or decorative elements to enhance the visual appeal.
“Creating a rain garden is a rewarding endeavor that not only enhances the beauty of your landscape but also contributes to sustainable water management practices.”
– Jane Anderson, Landscape Designer
By following these steps and considering these factors, you can design and construct a rain garden that effectively manages rainwater runoff, adds beauty to your landscape, and promotes a healthy environment.

Rain Garden Plant Selection and Care
Selecting and caring for plants in a rain garden is crucial for their long-term success. When choosing plants for your rain garden, it’s important to consider their ability to tolerate wet or dry conditions, their exposure to sunlight, and their water absorption traits. By selecting native plants that are well-adapted to your local climate and environment, you can ensure a thriving rain garden that provides numerous environmental benefits.
Native plants have evolved to thrive in their specific regions, making them better equipped to withstand local climate conditions and soil types. They are also more resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and unnecessary maintenance.
To assist you in making informed plant selections for your rain garden, here is a list of native plants that perform well in a variety of rain garden conditions:
| Plant | Height | Tolerance | Best Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|
| River Birch | 40-70 feet | Wet | Full Sun to Partial Shade |
| Redbud | 20-30 feet | Moist to Dry | Full Sun to Partial Shade |
| Buttonbush | 6-12 feet | Wet | Full Sun to Partial Shade |
| Switchgrass | 3-6 feet | Dry to Moist | Full Sun to Partial Shade |
| Bee Balm | 2-4 feet | Moist | Full Sun to Partial Shade |
These native plants have deep root systems that aid in water absorption, preventing erosion and creating a natural filtration system for rainwater runoff. They also provide food and habitat for local wildlife, contributing to the overall biodiversity of your rain garden.
Plant Care Guidelines
Maintaining your rain garden is essential for the continued health and effectiveness of the plants and ecosystem. Here are some tips for rain garden plant care:
- Regularly monitor your rain garden for weeds and remove them promptly to prevent competition for resources.
- Properly prune your plants to maintain their shape and promote healthy growth. Remove dead or damaged branches to prevent the spread of disease.
- Monitor for pests and diseases and take appropriate action if necessary. Consider using organic pest control methods to minimize the impact on the environment.
- During periods of prolonged drought or excessive rainfall, provide supplemental water or consider implementing additional rainwater management techniques to ensure optimal plant health.
- Periodically assess the overall health and functionality of your rain garden to identify any necessary adjustments or additions to the plant selection.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your rain garden remains visually appealing, environmentally beneficial, and low-maintenance for years to come.
“A rain garden design is more than just a beautiful addition to your landscape. It’s a sanctuary for native plants, a habitat for wildlife, and a sustainable solution for managing rainwater runoff.”
Final Thoughts for Rain Garden Design
Designing and implementing a rain garden design is a sustainable approach to managing rainwater runoff, promoting water conservation, and creating a resilient landscape. By following proper design principles, selecting native plants, and considering site conditions, you can create a functional and aesthetically pleasing rain garden that provides numerous environmental benefits.
Rain gardens are effective in reducing water pollution by capturing and filtering rainwater, preventing harmful runoff from entering waterways. They also help prevent erosion by controlling the flow of rainwater and promoting groundwater recharge. Additionally, rain gardens support local biodiversity by providing habitat and food sources for native plant and animal species.
Creating a rain garden requires careful planning and maintenance. By ensuring proper soil preparation, regular mulching, and monitoring, you can create an environment that conserves water and creates a green oasis in your landscape. Proper plant selection and care are also important to ensure the long-term success of your rain garden and its ability to support local ecosystems.
In conclusion, rain garden design and implementation offer a sustainable and effective solution for managing rainwater runoff, supporting water conservation efforts, and creating a resilient landscape. By incorporating these techniques into your sustainable landscaping practices, you can contribute to a healthier environment and enjoy the numerous benefits of rain gardens.
FAQ
What is a Rain Garden Design?
A Rain Garden Design is an innovative and sustainable landscape feature designed to manage rainwater runoff effectively. It captures, stores, and filters rainwater, reducing stormwater runoff and promoting groundwater recharge.
Where should a rain garden be located?
A rain garden should be placed where water naturally collects, avoiding utility lines or shallow foundations. The location should consider the flow of rainwater and potential obstacles like underground utilities or tree roots.
What are the benefits of using native plants in rain gardens?
Native plants are well-suited for rain gardens as they are adapted to the local climate, soil conditions, and water availability. They have deep root systems that enhance water absorption and prevent soil erosion. Native plants also provide habitat and food sources for local wildlife.
How do I create a plant list for my rain garden?
Creating a plant list for a rain garden involves selecting a variety of trees, shrubs, grasses, and perennials that are well-suited to the specific site conditions and fulfill the ecological functions of a rain garden. Consider selecting native plants that are tolerant to wet or dry conditions, sunlight exposure, and have the ability to support wildlife.
What are the benefits of rain gardens?
Rain gardens offer numerous benefits, including reducing water pollution, preventing erosion, and supporting local biodiversity. They prevent nonpoint source pollutants from entering waterways, nourish plants with collected rainwater, reduce flooding problems, and create habitats for wildlife. Rain gardens also conserve water and prevent erosion.
What are some common issues and considerations in rain garden design?
Poor drainage, erosion, steep slopes, and high costs are potential challenges in rain garden design. However, proper design, construction, and installation can address these issues. It’s important to conduct a water percolation test, choose appropriate rain garden elements, and consider site conditions.
How do I determine the size and depth of a rain garden?
The size and depth of a rain garden depend on various factors, including the drainage area, infiltration rate of the soil, size of the uphill drainage area, and amount of impervious surfaces. It’s important to consider the volume and intensity of rainfall, increase the size or depth if necessary, and use other rainwater management techniques if space is limited.
What factors should I consider when selecting a site for a rain garden?
Proper site selection is crucial for the success of a rain garden. It should be located between two impervious surfaces, such as a roof and a lawn, and away from utility lines and shallow foundations. The placement should consider the flow of rainwater and potential obstacles like underground utilities or tree roots.
How do I create a rain garden in my landscape?
Creating a rain garden involves selecting the right location, determining the size and shape, preparing the soil, and installing the garden. It’s important to dig a shallow basin or depression to collect rainwater and ensure proper drainage. The shape should be natural and rounded, and the plants should be perennial, as their deep roots aid in water absorption.
How do I select and care for plants in a rain garden?
Selecting and caring for plants in a rain garden is essential for their success. Native plants should be chosen based on their ability to tolerate wet or dry conditions, sunlight exposure, and water absorption traits. Regular maintenance, such as weeding, pruning, and pest monitoring, is crucial for the long-term health of the rain garden.